Uses a mold of sand packed around a
polystyrene foam pattern which vaporizes when molten metal is poured into
mold
§Other
names: lost‑foam process, lost pattern process, evaporative‑foam process, and
full‑mold process
§Polystyrene
foam pattern includes sprue, risers, gating system, and internal
cores (if needed)
§Mold
does not have to be opened into cope and drag sections
Figure
Expanded polystyrene casting process: pattern
of polystyrene is coated with refractory compound;
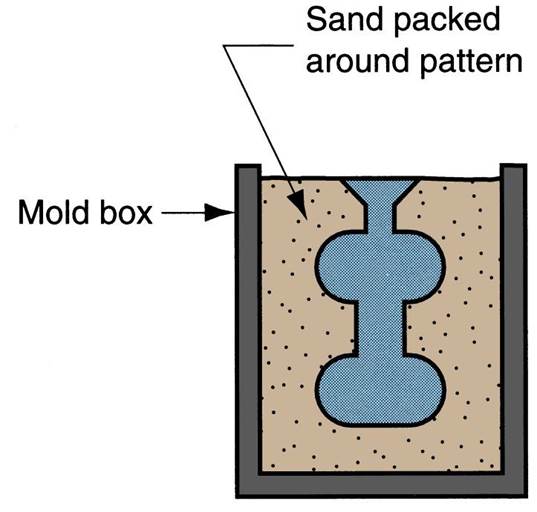
Figure Expanded polystyrene casting
process: (2) foam pattern is placed in mold box, and sand is compacted around
the pattern;
Figure
11.7 Expanded polystyrene casting
process: (3) molten metal is poured into the portion of the pattern that forms
the pouring cup and sprue.
As the metal enters the mold, the polystyrene foam is vaporized ahead of
the advancing liquid, thus the resulting mold cavity is filled.
Advantages
and Disadvantages
§Advantages of expanded polystyrene
process:
§Pattern
need not be removed from the mold
§Simplifies
and speeds mold‑making, because two mold halves are not required as in a
conventional green‑sand mold
§Disadvantages:
§A new
pattern is needed for every casting
§Economic
justification of the process is highly dependent on cost of producing patterns
Expanded
Polystyrene Process
§Applications:
§Mass
production of castings for automobile engines
§ Automated
and integrated manufacturing systems are used to
- Mold the polystyrene foam patterns and
then
- Feed them to the downstream casting
operation
Expanded polystyrene casting process: pattern of polystyrene is coated with refractory compound;
Figure Expanded polystyrene casting
process: (2) foam pattern is placed in mold box, and sand is compacted around
the pattern;
Figure
11.7 Expanded polystyrene casting
process: (3) molten metal is poured into the portion of the pattern that forms
the pouring cup and sprue.
As the metal enters the mold, the polystyrene foam is vaporized ahead of
the advancing liquid, thus the resulting mold cavity is filled.
Advantages and Disadvantages
§Advantages of expanded polystyrene
process:
§Pattern
need not be removed from the mold
§Simplifies
and speeds mold‑making, because two mold halves are not required as in a
conventional green‑sand mold
§Disadvantages:
§A new
pattern is needed for every casting
§Economic
justification of the process is highly dependent on cost of producing patterns
Expanded Polystyrene Process
§Applications:
§Mass
production of castings for automobile engines
§ Automated
and integrated manufacturing systems are used to
- Mold the polystyrene foam patterns and then
- Feed them to the downstream casting operation



ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق